Computational Materials Modeling & Simulation
Computational Materials Modeling & Simulation uses advanced mathematical models, physics-based simulations, and data-driven algorithms to predict how materials behave under mechanical, thermal, chemical, and environmental stresses. These methods help researchers understand material performance, optimize formulations, design new materials, and reduce the need for extensive physical prototyping.
By simulating phenomena such as stress–strain behavior, fracture mechanics, diffusion, thermal transitions, degradation, fatigue, corrosion, and molecular interactions, researchers can evaluate performance virtually, accelerating R&D, improving reliability, and reducing material cost and testing time.
Materials Metric integrates finite element analysis (FEA), finite element modeling (FEM), multi-physics simulations, thermal and mechanical modeling, molecular modeling, and degradation simulation, enabling a comprehensive understanding of materials ranging from polymers and composites to metals, ceramics, biomaterials, nanomaterials, and advanced functional materials and predicting material performance before physical testing.
Computational Materials Modeling & Simulation Can Achieve
1. Mechanical Behavior & Failure Prediction
Stress–strain curve simulation
Yield strength, fatigue life, fracture toughness, crack propagation
Predicting deformation, buckling, or creep under load
2. Thermal & Thermodynamic Modeling
Glass transition, crystallization, melting behavior
Heat distribution, thermal conductivity, thermal degradation pathways
Phase diagrams, reaction energetics, and thermal cycling effects
3. Molecular & Microstructural Modeling
Polymer chain dynamics, crystallinity, crosslink density effects
Nanoparticle dispersion and interfacial interactions
Grain boundary behavior, lattice defects, and anisotropy
4. Surface Interaction & Material Interface Modeling
Adhesion, friction, wear, and interfacial bonding
Protein adsorption and biological interface prediction (for biomaterials)
Coating integrity and delamination modeling
5. Diffusion, Transport, & Chemical Kinetics
Moisture absorption, solvent diffusion, or ion transport
Reaction kinetics and degradation pathways
Drug release and diffusion modeling for biomedical materials
6. Multi-Scale Modeling (Atomic → Macro)
Atomistic simulations (MD), microstructure (phase-field), and continuum modeling (FEM)
Integration of nanoscale features with macroscale performance predictions
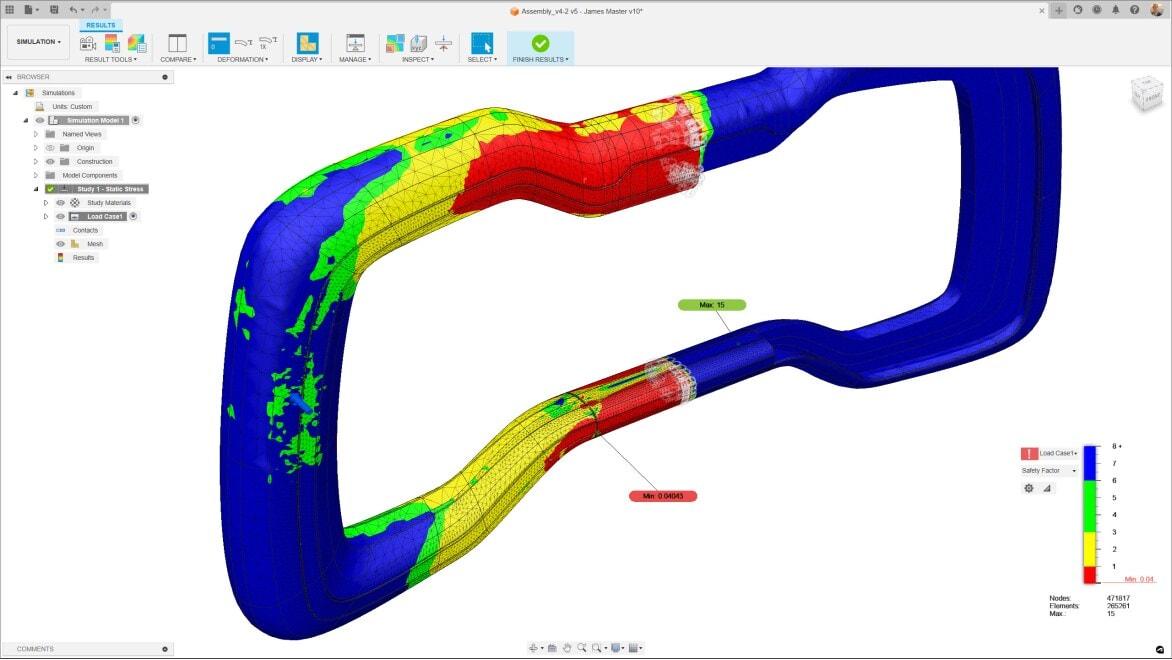

Applications
Advanced Materials & Polymers
Predict mechanical strength, elasticity, viscoelastic behavior
Model polymer curing, degradation, and recyclability
Optimize blends, additives, and stabilizers
Medical Devices & Biomaterials
Simulate implant–tissue interactions
Predict wear, fatigue, and surface degradation over time
Evaluate device performance prior to preclinical studies
Energy & Aerospace Materials
Thermal tolerance and heat shielding simulation
Corrosion, oxidation, and high-temperature mechanical behavior
Modeling composite structures for lightweight performance
Nanomaterials & Functional Surfaces
Modeling nano-patterned surfaces, coatings, and thin films
Predict optical, electronic, or catalytic properties
Evaluate nano–bio interactions (e.g., nanoparticles, sensors)
Pharmaceutical & Controlled Release Systems
Drug diffusion, dissolution, and release modeling
Stability, crystallinity, and moisture interaction prediction
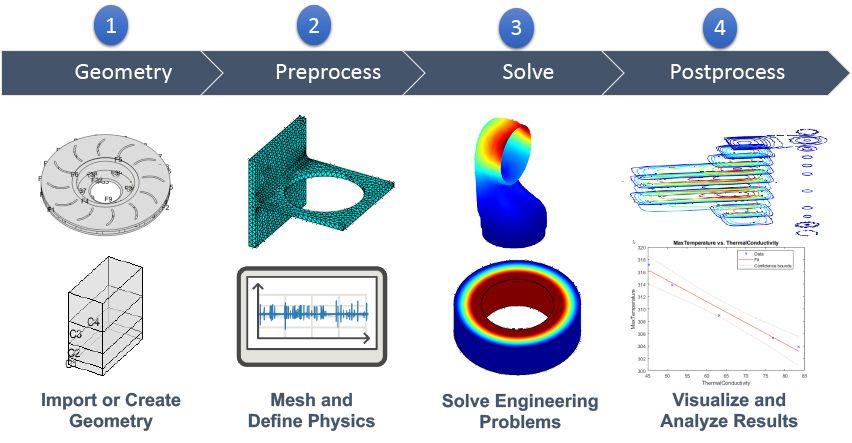
Computational Materials Modeling Workflow
1. Problem Definition & Data Intake
We identify target properties, environmental conditions, and performance criteria.
We gather material data from literature, experiments, or client datasets.
2. Model Selection & Setup
Selection of FEM, molecular modeling, thermodynamic models, or hybrid multi-scale approaches.
3. Simulation Execution
Mechanical simulation (static/dynamic loading)
Thermal, diffusion, or kinetics modeling
Atomistic or microstructural simulation
4. Post-Processing & Visualization
Generation of heat maps, contour plots, force distributions, molecular trajectories, and stress profiles.
5. Interpretation & Reporting
We provide a clear, structured summary including:
Key performance predictions
Failure risks
Recommended material modifications
Design optimization strategies
6. Integration With Experimental Data
Simulation results are paired with empirical testing (DSC, TGA, DMA, mechanical testing, spectroscopy) for validation and refinement.
Why Choose Materials Metric
Materials Metric offers a unique blend of computational modeling expertise and deep experimental capabilities, allowing us to ground simulations in real-world material behavior.
We provide:
ISO 9001:2015–aligned quality processes ensuring reliable, reproducible analytics
Cross-disciplinary scientific expertise spanning materials science, chemistry, biomaterials, simulation physics, and biomedical engineering
Multi-scale modeling capabilities, from atomic simulations to structural FEM
Seamless integration with laboratory testing including thermal, mechanical, spectroscopic, and surface analysis
Custom simulation solutions for complex materials, coatings, devices, and biomedical systems
Regulatory-supportive documentation suitable for design verification, risk assessment, and submission packages
Our simulations reduce development time, enhance design accuracy, and help companies innovate confidently.
Related services
